Lecture 14: Stop Loss and Take Profit in Smart Money Concepts (SMC) – Logical Placement Based on Liquidity & Structure
One of the most overlooked aspects of trading is proper stop-loss (SL) and take-profit (TP) placement. Many traders either place their SL too tight and get stopped out prematurely or place their TP randomly and miss out on potential profits.
Smart Money Concepts (SMC) emphasize logical SL and TP placement based on market structure, liquidity zones, and institutional behavior. By aligning stop-loss and take-profit levels with how the market moves, traders can avoid unnecessary losses and maximize profits.
In this lecture, we will cover:
- The importance of correct SL and TP placement
- Common mistakes traders make with SL and TP
- How Smart Money sets SL and TP levels
- Key concepts for SL: Liquidity zones, Order Blocks (OBs), and Market Structure
- Key concepts for TP: Liquidity targets, Fair Value Gaps (FVGs), and institutional levels
- Examples of correct SL and TP placement
Why Correct Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Placement Matters
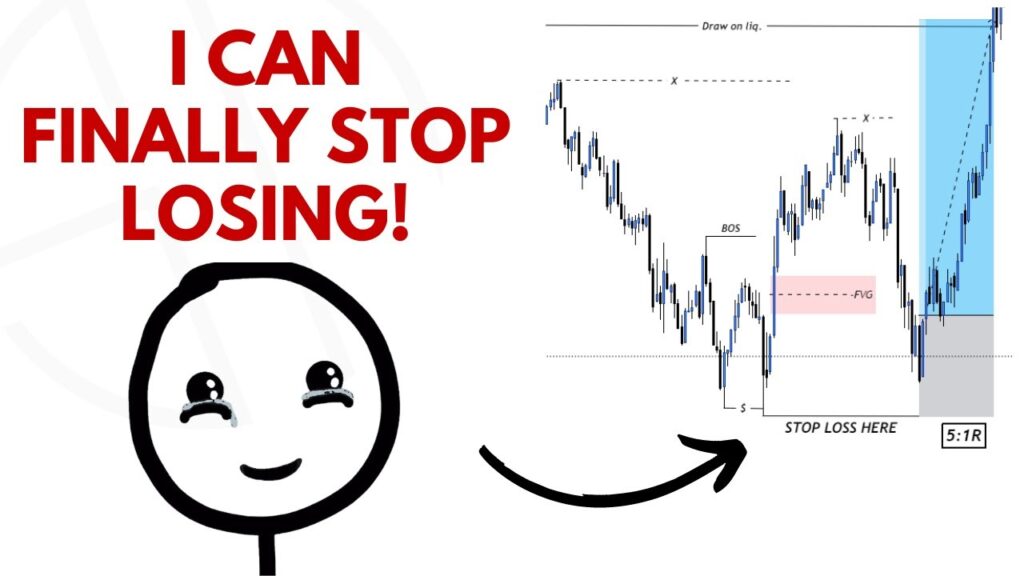
Stop-Loss (SL): Protecting Capital and Avoiding Early Stop-Outs
A stop-loss is designed to protect a trader from excessive losses, but if placed incorrectly, it can lead to frustrating stop-outs before the trade moves in the expected direction. Retail traders often place SLs too close to entry, making them easy targets for liquidity grabs.
Smart Money traders, on the other hand, place SLs strategically in areas where:
- Liquidity is swept, ensuring that their SL is not part of the manipulation.
- Market structure confirms that price should not return to that level if the setup is valid.
- Institutional traders are unlikely to push prices back into their position.
Take-Profit (TP): Maximizing Profit While Avoiding Greed
Take-profit levels should be based on liquidity targets rather than random price points. Many traders take profits too early due to fear or hold onto trades too long hoping for more gains, only to watch their profits disappear.
Smart Money traders set TP levels where:
- The market is likely to reverse due to liquidity resting at key highs or lows.
- Institutional traders are taking profits, causing prices to slow down.
- A trade reaches a logical Risk-to-Reward (R: R) ratio, such as 3:1 or 5:1.
Common Mistakes with SL and TP Placement
Stop-Loss Mistakes:
- Placing SL too close to the entry
- Example: A trader enters a trade based on a 4H Order Block (OB) but places their SL just a few pips below. Price often sweeps that level before moving in the intended direction.
- Using fixed pip-based SL instead of structure-based SL
- Some traders always use a 10-pip or 20-pip SL instead of analyzing market structure. Smart Money does not care about fixed pips; it focuses on structure.
- Placing SL inside liquidity zones
- Example: A trader shorting at resistance places their SL just above a recent high. This is exactly where Smart Money grabs liquidity before reversing.
Take-Profit Mistakes:
- Taking profit too early
- Fear of losing small profits causes traders to exit before the real move happens.
- Not identifying liquidity targets.
- Example: Instead of setting TP at a key previous high/low, traders pick a random level, missing a much bigger move.
- Ignoring Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) and Institutional Levels
- Example: If the price is moving in a trend, it often aims to fill an FVG before reversing—an ideal TP target.
How Smart Money Sets Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels

Stop-Loss Placement – Key Concepts
- Below/Above Structural Lows and Highs
- If entering a long trade, place SL below the most recent structural low where liquidity has likely been swept.
- If entering a short trade, place SL above the most recent structural high where Smart Money has taken liquidity.
- Beyond the Order Block (OB) or Fair Value Gap (FVG)
- If entering a trade based on an Order Block (OB), place SL below (for buys) or above (for sells) the OB to avoid premature stop-outs.
- If the price re-enters the OB significantly, the setup is likely invalid.
- Below/Above Inducement Levels
- Inducement levels are areas where retail traders are lured into the wrong direction before a real move occurs.
- Smart Money traders place their SL outside of these zones to avoid being trapped.
- Logical Risk-to-Reward Ratio (R: R )
- If the trade does not allow for at least a 2:1 or 3:1 risk-reward ratio, reconsider the entry.
Take-Profit Placement – Key Concepts
- Targeting Liquidity Pools
- Price moves towards liquidity pools, which are areas where large amounts of stop-losses and pending orders are placed.
- These areas are usually at:
- Previous swing highs and lows
- Double tops and double bottoms (retail trader stop zones)
- Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) and Imbalance Zones
- If the price is filling an FVG, set TP at the other end of the gap.
- FVGs act like magnets where price seeks to rebalance.
- Big Figure Levels and Institutional Levels
- Banks and institutions often take profits at psychological levels like 1.1000, 1.2000, etc.
- These areas tend to act as strong reversal points.
- Trailing TP Strategy
- Instead of setting one TP level, Smart Money traders scale out by:
- Closing partial profits at first liquidity targets
- Letting the rest of the position run using a trailing stop
- Instead of setting one TP level, Smart Money traders scale out by:
Example of Proper SL and TP Placement
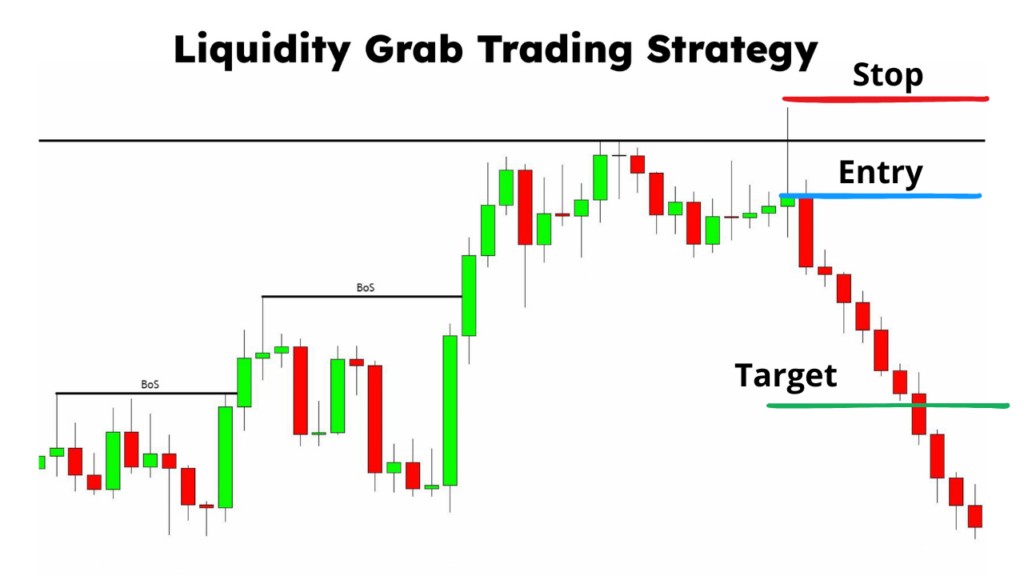
Bullish Trade Example (Buy Entry at Demand Zone):
- Higher Timeframe Confirmation:
- The 4H chart shows the price in a bullish trend and approaching a demand zone with an Order Block.
- Lower Timeframe Refinement:
- 15M and 5M charts show a liquidity grab and Break of Structure (BOS), confirming a potential reversal.
- Stop-Loss Placement:
- SL is placed below the recent low where liquidity was swept, ensuring Smart Money does not stop the trade.
- Take-Profit Placement:
- First TP: Previous swing high (liquidity target)
- Final TP: At a Fair Value Gap completion level
Conclusion
Proper SL and TP placement is not random; it follows logic based on liquidity, market structure, and institutional behavior.
- SL should be placed beyond liquidity grabs and structural invalidation points to avoid being stopped out early.
- TP should be set at liquidity targets, Fair Value Gaps, and institutional levels to capture maximum profit.
By mastering these concepts, traders can significantly improve their risk management and profitability, aligning themselves with Smart Money rather than falling for retail traps.
How useful was this article?
If you'd like more tips on how the "Smart Money" trades, learn one of the most powerful trading signals, download this Strategy Guide.
Until next time,
The Trading Strategies Team